Basics of Die casting Process Production
Die casting process is a branch of mechanical engineering engaged in the manufacture of blanks or parts by pouring molten metal parts into a special aluminum alloy, the cavity of which has the shape of a blank. The final product is called casting.
Aluminum die castings Introduction
When aluminum die castings under pressure, a metal aluminum alloys in a liquid or solid-liquid state is fed into the pressing chamber of a special machine, from where, under a pressure of 20. . .250 MPa, created by a piston moving in this chamber, at a speed of 1 to 60 m / s through a thin (0.1 … 0.3 mm) slotted feeder fills the cavity of a heated and lubricated aluminum die cast parts and hardens in it.

For the manufacture of castings, many casting methods are used:
- in sand molds;
- investment models;
- in a chill aluminum alloy;
- under pressure;
- centrifugal casting, etc.
The scope of a particular casting method is determined by the volume of production, the requirements for the geometric accuracy of the surface roughness of the casting, economic feasibility, and other factors.
Classification of cast blanks
According to the operating conditions, regardless of the method of manufacture, castings are distinguished:
- general purpose group – for parts not calculated for strength. Their configuration and dimensions are determined only by constructive technological considerations;
- a responsible group makes castings for the manufacture of parts calculated for strength and operating under cyclic and dynamic loads;
- a group of castings for especially critical purposes is used for the manufacture of parts calculated for strength and operating under cyclic and dynamic loads.

Depending on the manufacturing method, weight, surface configuration, maximum overall dimensions, wall thickness, number of rods, purposes and special technical requirements, castings are divided into six groups of complexity.
1. Kinds of high pressure injection molding equipment
Injection molding machines come with hot (piston and compressor) or cold (piston) compression chambers. Piston machines can have a vertical or horizontal bale chamber. Three schemes and, accordingly, three types of injection molding machines have become widespread:
- with a cold horizontal bale chamber;
- with a cold vertical pressing chamber;
- with hot vertical chamber.
Cold Die Casting Process
In machines with a cold horizontal chamber the aluminum die cast parts consists of a fixed 6 and 4 movable halves. The first is attached to the fixed plate 7 of the machine, and the second to the movable plate 1. Molds can have channels 5 for water cooling.
The rods 3 (metal parts) for the formation of cavities and holes in the aluminum die castings are, as a rule, in a movable half-mould. To extract the aluminum die castings from the aluminum alloy, ejectors 2 are provided, which are rigidly fixed in the ejector plate.

The locking mechanism of the machine reliably presses the movable aluminum alloy half to the stationary one, after which a portion of the alloy is poured into the cylinder 8, called the pressing chamber, through the hole 13 and the pressing mechanism is turned on.
Plunger 9 closes the filling hole and creates pressure in the chamber. The alloy fills the mold cavity through the sprue slot and hardens.
As soon as the die casting manufacturing process hardens, the movable part of the mold is withdrawn together with the aluminum die casting. Together with the movable part of the mold, plunger 9 moves, which pushes the press residue 10 out of the pressing chamber?
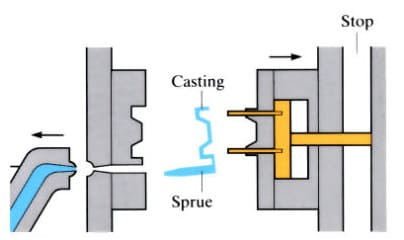
The pusher plate moves with the mold until it stops 11. The stop stops the pusher plate, and the mold continues to move. The ejectors “remove” the die casting manufacturing process12 from the rod 3, and it falls onto the conveyor or into the container. The mold is blown with compressed air, the working surface is lubricated, closed, and the process is repeated.
2. Low pressure aluminum die castings machines
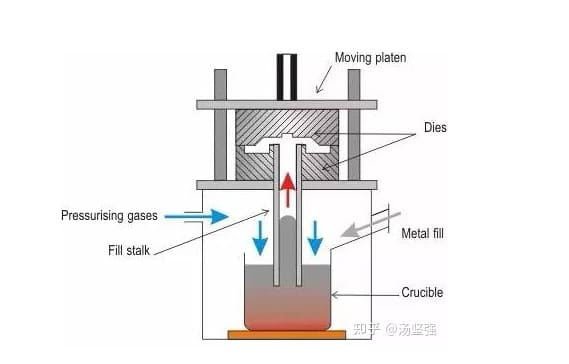
Machines in which the metal moves under the action of compressed air are called compressor machines or low-pressure aluminum die casting equipment. The principle of their operation is that compressed air presses on the surface of the metal in the crucible, from which it enters the mold through a metal conduit.
Fixed wire compressor injection molding machines have a large surface area of molten metal that is pressed against by compressed air. This leads to the oxidation of the melt and does not allow the pressure to rise above 60 Pa.
Unlike them, in machines with a movable metal wire, air presses on a small metal surface, which makes it possible to increase the pressure to 400 Pa and sharply reduce the liquid metal oxidation surface.
Complex Designs of low pressure aluminum casting process
The complex designs of the low-pressure aluminum die casting processes machine:
· 1, an upper movable plate for installing the upper half-mould
· 2, a rotary aluminum die casting remover
· 3. This machine is made according to the scheme of a compressor machine.
· 4, cylinders fixing the lower half of the mold
· 5, the machine table for installing the lower half of the mold
· 6, the base of the machine
· 7, the furnace for melting metal
· 8, the furnace lifting system for precise joining of the metal wire of the furnace and the mold
· 9. The working area is closed by a protective cover
Such machines are designed for the manufacture of aluminum blanks with increased strength characteristics in automatic mode. The control system is made on a programmable controller. The cycle of the low pressure aluminum die casting machine includes:
- stilt stop;
- filling out the form;
- mold cooling;
- opening the halves of the mold and feeding the rotary puller of the aluminum die castings;
- ejection of the aluminum die casting from the mold

The machine has devices for temperature control of the furnace and maintaining the required pressure in it. For accurate dosing of metal during the aluminum die casting process, a multi-stage injection system is used, which depends on the complex designs of the aluminum die casting.
Low pressure aluminum first die casting equipment operating according to the scheme shown in fig. 9, a, due to the significantly reduced gas segregation in the aluminum die casting, they are widely used.
3. Pressing unit of injection molding machines
The main mechanism of the injection molding machine is the pressing unit. Most of the machines are equipped with pressing mechanisms with pressure multiplication of the working fluid during the period after pressing, called pre-pressing.
In such machines, the same battery is used to move the press piston and the multiplier piston. When designing it, they try to achieve a high pressing speed and a minimum pre-pressing time.
Mechanism of Die casting
The mechanism consists of a pressing cylinder 4, a press piston 3, a multiplier 10, a multiplier piston 11, an accumulator 7; a check valve 9, travel switches 1 and 2, valves 6 and 8, a multiplier accumulator 5 and a rod 12. The multiplier is attached vertically to the pressing cylinder, and the piston accumulator 7 is installed directly on the pressing cylinder 4.

It provides the second and third phases of pressing, and the first phase is carried out by supplying liquid with a pump (arrow A). The manual valve 6 adjusts the pressing speed, and the valve 8 adjusts the pre-press time. The rod 12 allows you to control the stroke of the multiplier piston and the moment it starts to move.
Mechanisms with a single battery have a simpler design, but depend on the technological parameters of the aluminum die casting. Low speeds lead to an increase in pre-pressing time, which reduces the technological capabilities of the mechanism.
Mechanisms with two accumulators are more complex in design, but in them the pre-pressing time does not depend on the pressing speed.
What is press mechanism?
In press mechanisms with a multiplier, the inertia of the piston leads to an increase in prepress time and increased pressure peaks during the transient process, therefore press mechanisms without a multiplier have been developed and manufactured.
They use high pressure accumulators to perform prepress. An example of such a mechanism is the Fries pressing mechanism.

In the first phase, the liquid from the accumulator 5 through the valve 7 through the channel 8 is supplied to the piston cavity of the pressing cylinder 1, informing the press piston 11 of slow movement.
The speed of the press piston in this phase is controlled by valve 7. This phase continues until the rear end of the press piston 11 opens channel 9. After that, the second pressing phase begins, which continues until the chamber is filled with metal.
On command from the limit switch, valve 6 opens and the press piston begins to move rapidly. To control the pressing speed in the third phase, the valve regulator 6 is used.
The limit switch, which is adjusted depending on the path of the press piston 11, turns on the fourth phase – prepressing. At this time, valve 2 opens and liquid from the high pressure accumulator 3 enters the piston cavity of the pressing cylinder.
The check valves 10 and 4 are closed, and the high-pressure fluid from the accumulator 3 is transferred to the piston cavity of the cylinder 1, carrying out prepressing. The multiplication pressure is regulated by changing the pressure in the accumulator 3; the valve regulator 2 is used to set the prepress time.
The mechanism has all the disadvantages that mechanisms have with the inclusion of a pre-compression device along the path of the press piston.
Injection molding machines most often operate in semi-automatic mode.
Additionally, the following operations are mechanized and automated:
- lubrication of the molds of the pressing chamber and the machine;
- heating or cooling of half-forms;
- extraction of the aluminum die casting and transporting it from the machine to the cutting press;
- feeding a portion of the liquid alloy into the pressing chamber (pneumatic, magnetodynamic or mechanical manipulator);
- replenishment of the crucible with liquid metal (for machines with a hot pressing chamber);
- installation of reinforcement in the form.
The main means of automating injection molding processes is the use of molten metal dispensers, which can be of several types:
- pneumatic;
- mechanical rotary;
- mechanical on a monorail

4. Injection molding machine dispensers
Pneumatic dispensers for aluminum alloys models operate on a principle similar to that used in low-pressure aluminum die casting equipment, when compressed air presses on the surface of the molten metal and displaces it into the feed tray into the chamber pressing a aluminum die casting machine.
These machines can dispense metal weighing from 4 to 70 kg in a time of 5 to 30 s, while allowing an error of no more than 3%. This dispenser includes a melting furnace, pressurizing pumps and an automatic dosing device.
During operation, the ladle is immersed in the melt and the metal is transferred to the opening of the pressing chamber of the injection molding machine, where it overturns. Similar dispensers can also be used to automate centrifugal aluminum die casting machines.








