Die Casting: what is it and how does it work?
Casting is the manufacturing process of metal parts in which the cavity of a mold is filled with liquid metal, with dimensions and format equivalent to those of the part to be produced.
This is one of the most versatile and ancient processes, especially when considering the different shapes and sizes of parts that can be produced using it.
Die casting Advantages and Disadvantages
The main advantage is to obtain, in an economical way, complex parts. Die castings can be made of ferrous or non-ferrous materials.
It is an initial manufacturing process especially small scale production because die casting makes it possible to obtain pieces with practically definitive shapes, with minimal limitations in terms of format, size, and complexity. This is the process by which ingots are manufactured.

And it is from the ingot that the mechanical conformation processes are made to obtain plates, sheets, profiles, etc. The high pressure die casting process applies to several types of metals, such as cast iron, steel, aluminum, copper, magnesium, zinc, and their alloys.
However, there are also disadvantages. For example, cast steels can exhibit high residual stresses, zoning, microporosity, and grain size variations.
The result is lower strength and ductility when compared to steels resulting from other manufacturing processes, such as hot forming.
What are the uses of high pressure die casting?
Some examples of die castings: are automobile and aircraft engine blocks, pistons, piston rings, machine tool bases, wheels, furnace parts, piping fittings, and crankshafts.

Feedstock
The die castings are produced using raw materials of ferrous metal alloys (carbon and iron alloys) and non-ferrous metal alloys (aluminum, zinc, copper, and magnesium alloys).
Bottom of Form
Die casting parts manufacturing process
We can summarize the manufacturing process of these parts through die casting in the following steps:

Model creation
It consists of manufacturing a model with the approximate shape of the part to be cast. This model will be used for the construction of the mold, and its dimensions need to predict the contraction of the metal when it solidifies, in addition to any excess metal for subsequent machining of the part.
It is usually produced in wood, aluminum, steel, plastic resin, and even styrofoam.
Mold production process
It is the device into which molten metal is inserted to obtain the desired part. The mold is made of refractory material, composed of sand and binder. This material is molded over the model, and after being removed, it leaves a die cavity in the shape of the part that will be cast.

Male production process
The core is a device, also made of sand, with the purpose of shaping the voids, holes, and recesses of the part. They are used in the molds before they are closed to receive the molten metal.
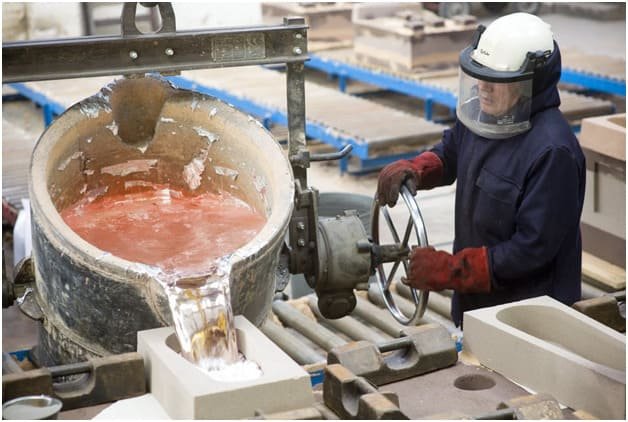
Fusion
This is the stage where the low melting point of the metal occurs.
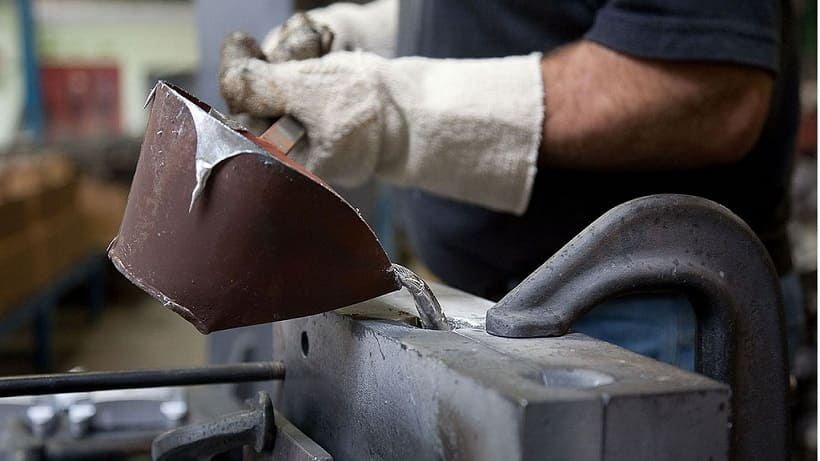
Leak
It is the filling of the mold with liquid metal.

Unmold
After a certain period of time in which the part solidifies inside the mold, which depends on the type of part, the metal (or metal alloy), and the type of mold, it is removed from the mold (demolding) through mechanical processes or manually.
Deburring
It is the removal of feed channels, burrs, and risers that are formed during die casting technology. The deburring is done when the part reaches temperatures close to those of the environment.
Cleaning
It is necessary because the part has a series of incrustations from the sand used in the large scale production of the mold. Usually, it is done through abrasive jets. This sequence of steps is generally followed in the most commonly used gravity sand casting process. A very common example of a product that is manufactured through this process is the engine block of automobiles and trucks.

What are the types of high pressure die casting?
Gravity die casting
It basically relies on gravitational force to help fill and solidify metal parts. The use of sand molds, for this, has become quite popular, as they are economical and simple to manufacture.
This economy comes from the reuse of this sand, after sifting, reaching up to 98% recycling. This demonstrates its great capacity for mass production and reuse.
To achieve precision in finishing, the furnace needs to be suited to the technique chosen and the metals or alloys used. Temperature and time control must be precisely adhered to.

Sand casting
It is the simplest and most used process in foundries today. In sand casting, it is necessary to carry out compaction of a plastic refractory mixture (high pressure die casting sand).
This mixture is made with compounds that will be used to manufacture the mold and form the part. The compounds may vary according to the need for finishing and the type of sand chosen.

Molds made with dry sand, for example, provide a surface finish and are more permeable compared to green sand molds. On the other hand, green sand molds are cheaper, as they are the clay, siliceous sand, and water.
In both cases, after the mold cavities are produced, the metal will leak into the interior, giving shape to the pattern marked in the sand.
Permanent mold casting
They have permanent parts and temporary parts, which can be broken after the melt solidifies. Permanent molds must be made with a metal that has a higher melting point compared to the metal of the part to be produced.
Due to their high cost, these molds are usually made only for the production of parts in series, because a single mold is capable of producing up to 100,000 parts.
Although it is a high number, it is not possible to use this method in all types of metal casting, as its use is limited to metals with lower melting temperatures than iron and steel.

Centrifugal die casting
High pressure die casting process in which cylindrical or symmetrical parts are manufactured and consist of pouring the liquid metal into a mold that will make the rotation movement.
The centrifugal force, which results from the rotation of the mold, forces the metal to enter under pressure. That way the metal fills in the small sections and maintains good contact between the metal and the molding.
As advantages of centrifugal casting we have:
· Good surface finish.
· Decrease (or eliminate) channel systems.
· Possible use of a wide variety of metal types.
· Directional solidification.
Precision casting
Precision is the characteristic that differentiates this process from other types of die casting. Because of this, this high pressure die casting is widely used in parts with complex levels of detail, such as turbine blades and medical equipment.

The advantages of this casting process are:
· Excellent surface finish, with no need for machining.
· Reproduction of details, thin walls.
· Parts without parting lines.
· Shape flexibility.
· Narrow dimensional tolerance (0.08 mm).
There are also some limitations in this type of high pressure die casting, such as the weight limit, considering the high cost and the capacity of the available equipment.
It is also necessary to have strict control of all its steps to ensure the desired accuracy.
What are the main advantages of the high pressure die casting process?
Do you know the main advantages of the die casting process and do you know why it has been gaining more and more space when compared to other manufacturing methods with metals?
High pressure die casting is an ancient process developed by man to transform metal into machines, utensils and different objects. Many times, we use items from the high pressure die casting process, without even realizing it.
According to historians, the most primitive die casting processes appeared more than 6,000 years ago, when humanity began to develop its first metallic utensils, initially with copper and bronze, which have a low pressure casting and melting point.

In the middle Ages, cast metals were already used on a large scale for the manufacture of weapons of war, while in the period of the industrial revolution, steel gained space in the high volume production of machinery and equipment.
The high pressure die casting process basically consists of heating the metal at high temperatures until at its melting point the metal changes its solid state to a liquid state.
When in the liquid state, the metal is placed in a mold that has the desired shape for the part to be produced. After the metal has cooled and solidified, the mold is removed and the pre-molded part undergoes finishing processes.
What are the main advantages of the high pressure die casting process?
Casting is one of the most used techniques for the manufacture of metallic parts and components.
The choice of die casting in general is related to the greater safety, higher precision, and final quality offered by the process, which allows the manufacture of continuous complex shapes (in full) without the need for splicing or welding points.

Check out the main advantages of the high pressure die casting process below:
- The part with large volumes is already ready for machining and/or assembly;
- Low risk of warping;
- Possibility of manufacturing in special steel and iron alloys (specific to each project);
- Easy manufacturing in gray and nodular cast iron alloys;
- When steel is replaced by cast iron, there is a reduction in the weight of the parts, due to the difference in densities;
- After creating the model, manufacturing becomes fast;
- Reduction in the need for specialized internal labor.
The casting process is one of the oldest and most versatile in the area of metallurgy , which, in addition to shaping, determines the mechanical and physical properties of the part.
Due to the need to manufacture parts with mass production in cold chamber die casting, it is one of the most used techniques in the manufacture of metallic parts and components, industries have been investing in the casting process due to its versatility, which allows obtaining different dimensions in the most diverse geometric formats and complexities.
The high pressure die casting process basically consists of producing parts in the desired shape, through liquid metal placed in molds that, after cooling, solidify resulting in a semi-finished or finished part.

Advantages and disadvantages
Casting is a technique for manufacturing parts of various types of metals and alloys, taking them to a high temperature and leaving them in their liquid state (molten).
After that, these are placed in a mold with a cavity (permanent or disposable form) in which the worked metal will cool and solidify in a projected shape. Finally, after it is removed from the mold becoming a casting.
It is considered the simplest and most economical process for producing parts, from the simplest to the most complex, of different sizes, dimensions, and geometries. Thus, it gives rise to semi-finished or finished pieces.
The casting process also serves to make surface finishes with forming processes, welding processes, machining, deburring (chips), and heat treatment.
Application examples: piping accessories, engine block, cylinder heads, piston rings, machine tool bases, wheels, axles, etc.
See the steps of the high pressure die casting process:
- Mold making via heat treatment: a model of a part made of wood, metal, plastic resin, styrofoam, etc., which can be permanent or non-permanent to shape the casting.
- Manufacture of cores: they are models of parts made of different resistant materials that form channels or holes in parts that need to be poured (empty space) and that can be broken for the part to come out after solidification and cooling.
- Melting of the metal : it is the change of state of the raw material from solid to liquid, caused by the high temperature (heat) reaching its melting point around 1530ºC.
- Pouring (filling): the pouring of the liquid material into the mold cavity and through the channels, where it will wait for the cooling to solidify.
- Unmolding: the removal of the part manually and mechanically from inside the molds after solidification and cooling.
- Finishing (burring and cleaning): is done by wire brushes, grinders, sanders, abrasives, cutting tools, and other tools.
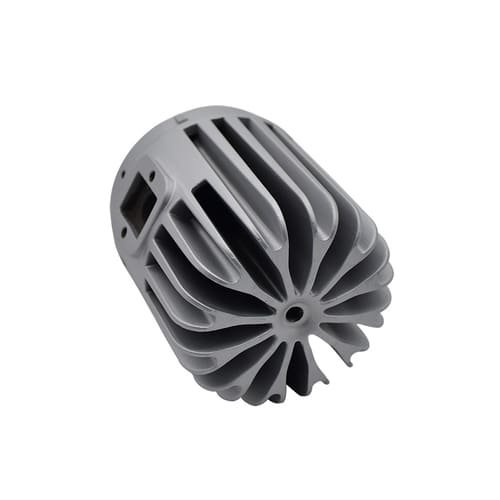

Note: the composition of the metal, its resistance and the number of parts to be produced must be taken into account.
Now that you have known a little about foundry processes, you can see that they have their application particularities, which must be taken into account in each of their stages:
- mold making
- manufacturing of male molds
- metal fusion
- leak
- disassembly
- finishing
In which the most common other casting processes are casting by:
- Gravity
- Centrifugation
- Pressure
- Precision or lost wax
The choice of the process that will determine the final part designed, what differentiates is the way the liquid metal is poured and the type of molding used, seeking to meet the specific needs of applications for each client.

Where to find custom castings in 2022?
Make your quote for custom castings with Castingod.
We have been offering professional casting and machined solutions with reliability, technology, and excellence in accordance with the needs of our customers.
Our constant evolution and experience result in today in a solid company, service to a wide range of products, with qualified professionals, and in the success of our partners.
We offer personalized service and develop solutions for your specific needs; after all, each client is unique.







