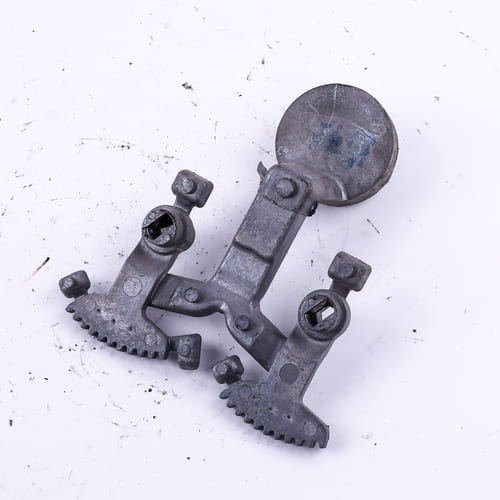
Aluminum as strong as steel
Aluminum is one of the most promising materials for the aeronautical and automobile industries.
The aluminum die casting process is one of the oldest for processing this metal. With a low melting point considered low, around 660°C, aluminum stands out for having a wide range of uses and a relatively simple casting process.
In this article, we will present some of the main existing processes.
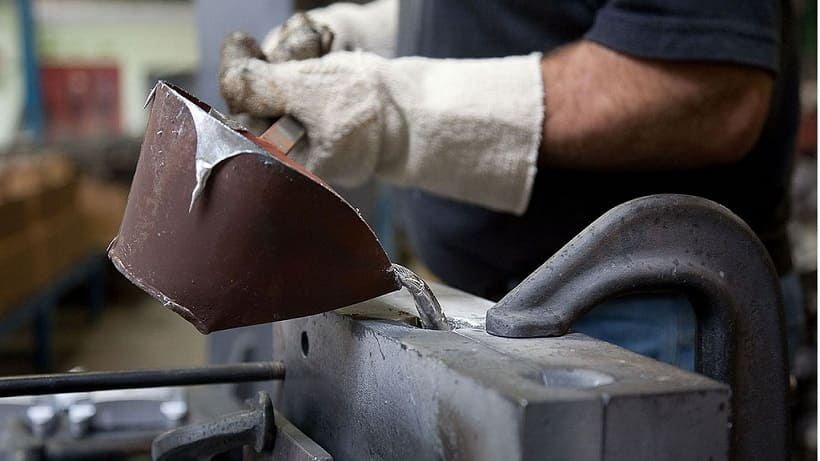

ALUMINUM CASTING PROCESSES
Among the foundry processes we can highlight:
Aluminum Casting in Sand and Steel Chill: In this process, the aluminum flows to be filled by gravity, from the mass-batch (die casting channel). The great advantages of this process are a relatively low initial cost, medium repeatability and a wide range of possible geometries to be copied. Its disadvantages are the real threat of porosity and other flaws (cold welds, sinks, peelings) and, sometimes, filling failure.
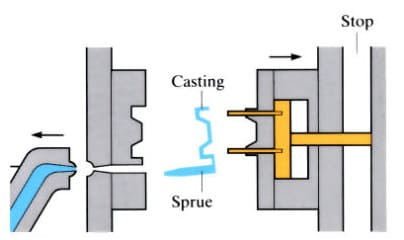
Aluminum casting in Metallic Matrix:
In this process, aluminum is injected with great pressure to reach the total filling of the aluminum die casting and to be able to reproduce the most specific details. This process is widely used in the automotive industry and on parts with significant detail and thin walls that need to be copied with precision and dimension accuracy.
The advantages of injected parts are the excellent surface quality and finish, the precision of the details, practically free of porosity and the high repeatability. Its disadvantages are the high initial cost, due to having to produce a steel matrix for the die casting, and the restriction on the die casting alloys to be used.
Die Casting Aluminum:
In this process, aluminum is gravitationally poured over aluminum die casting in a press and, after this pouring, pressure (between 6 and 8 bar) is injected into the still liquid aluminum.
This pressure difference between the center of the molten aluminum block and the surface of the block in contact with the atmosphere makes air residues and other gaseous porosities tend to go to the surface of the blocks.
Thus, most of the porosities are forced out of the block, leaving the material homogeneous and practically free of porosity. The advantages of this process are the high range of alloys that can be applied to it, the variability of geometries capable of being copied and a very low initial cost, since high cost matrices or aluminum die casting are not required.
CAST ALUMINUM: PERMANENT MOLD CASTINGS AND RESISTANCE PATTERNS
All of the above processes, some more, some less, are based on a good flow of molten aluminum to be able to fill during the aluminum casting process and correctly copy the part and, for this to happen, the presence of silicon (Si) in the alloy is necessary aluminum. Silicon guarantees good flow to molten and liquid material, ensuring filling.
Silicon-based die casting alloys are the most used in foundry processes as mentioned above. Even so, Metalthaga was able to develop cast alloys with high levels of magnesium die casting (Mg) and zinc (Zn) for the market. These alloys can guarantee the piece higher standards of mechanical strength and elongation.

Aluminum is one of the most used metal alloys in the world and its manufacturing process has been present in human history for many centuries. All this is the result of the ease of working with the material, because its melting point is considered low (600º C) and still allows for a range of works.
Aluminum smelting is part of the advancement of our society and nowadays it is one of the most important elements in several industrial segments.
WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF ALUMINUM CASTING?
There are three main types of aluminum casting: the first is sand and steel casting; the second in metallic matrix; the third in under pressure. Below we present a more detailed content of each type. Follow!
Aluminum casting in sand and steel permanent mold casting
It is a process in which aluminum is drained by gravity for filling. It starts with mass-batch, or die casting channel, and its main advantage is that the initial costs are considered low. Furthermore, the repeatability is rated average and there is still a range of possible geometries that can be replicated.
On the other hand, the disadvantages relate to porosities that may arise in the process and other types of failures, such as cold welds, holes, sinkholes, etc. When the casting is deficient, the act of filling itself can also be compromised.
Aluminum casting in metal matrix
The aluminum is injected so that the filling takes place in the entire area of the aluminum die casting, a job done with great pressure to guarantee the best result. In this way, it is possible to reproduce much more specific details, especially if we compare it with the first type of aluminum casting mentioned in the previous paragraph.

It is a common process in the automotive industry, particularly for creating parts with essential detail and thin walls that require perfect copying and exact dimensions.
is one of the first industrial processes used in the production of die cast metals or aluminum cast parts. The properties of aluminum and modern technology offer excellent conditions, with adequate scientific controls, so that large quantities of cast aluminum parts can be produced while maintaining uniform quality. The market has excellent aluminum alloys that provide a wide variety of properties for castings. The main ones are:
· Low melting temperature
· Strong tendency to oxidation
· Low density
· High thermal conductivity
· High coefficient of expansion.
Preparing Aluminum Die casting mold
The pouring of liquid metal into sand permanent mold castings is one of the oldest industrial arts. It is still used when castings are required in small quantities, exceptionally large in size or very intricate. Cast aluminum parts with better surface finish are produced by gravity die casting.
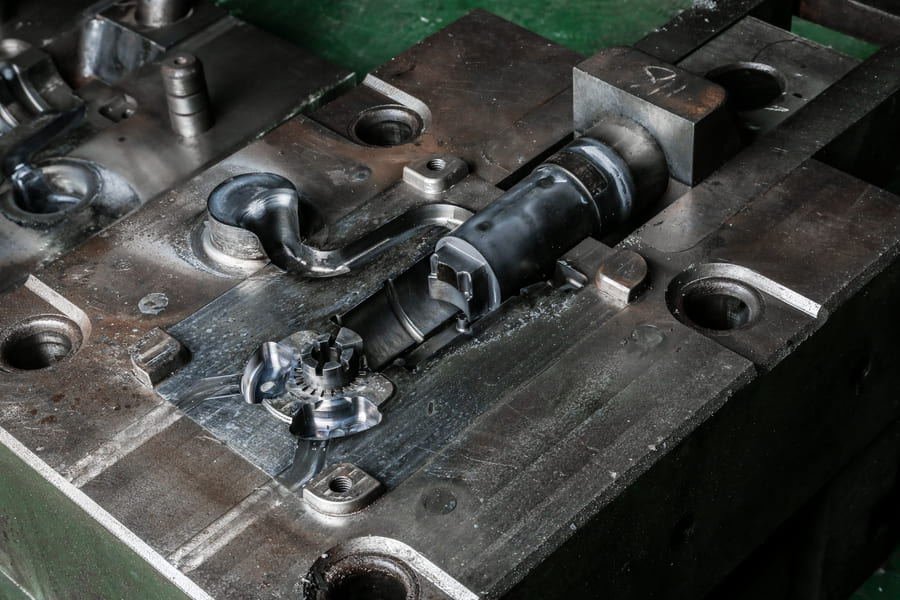

The metal is poured into an iron or steel matrix. This process becomes economical when there is a demand for a considerable number of cast aluminum parts.
For large volumes of cast aluminum parts, die casting under pressure is the most advantageous. Metal is forced into steel dies under the force of hydraulic pressure. Castings with great accuracy of detail are produced in this way. The method has been increasingly used in castings up to the size of cylinder blocks.
Cast Aluminum Parts
On the other hand, when a high degree of dimensional accuracy is required, but the number of cast aluminum parts is relatively small, an older process is used: lost wax. In it, a consumable model is coated with a thin refractory layer, which is subsequently oven-hardened to form the cast iron casting. The figure below shows a series of castings.

Cast Aluminum have their main applications in the automotive and transportation areas, which represent around 60% of aluminum consumption in this segment. As an example, one can cite engine blocks, gearboxes, engine frames and wheels for automobiles and heavy vehicles, among others.
Casting can be done by gravity, using sand or metallic permanent mold casting, and under pressure (high or low). In addition to these, there are also special processes, with lost wax and centrifugal casting.
Sand casting Process
It is a process that can be done by permanent mold casting in green sand and shell shells, cold curing, with carbon dioxide and loast foam. Green sands are sands agglomerated with clay in the wet state. This material consists of refractory granules called base sands and a product with cohesion and plasticity capacity – the binder – which in this case is clay.
Foundry sands can be natural, semi-synthetic (with additions to correct or improve natural properties) and synthetic (obtained by mixing the basic constituents separately, such as sand, binders, additives and plasticizers).
Die casting
Made by gravity, this process consists of obtaining cast aluminum parts by pouring liquid metal into a metal permanent mold casting, also called a cast iron casting. The introduction of metal is essentially determined by the force of gravity.
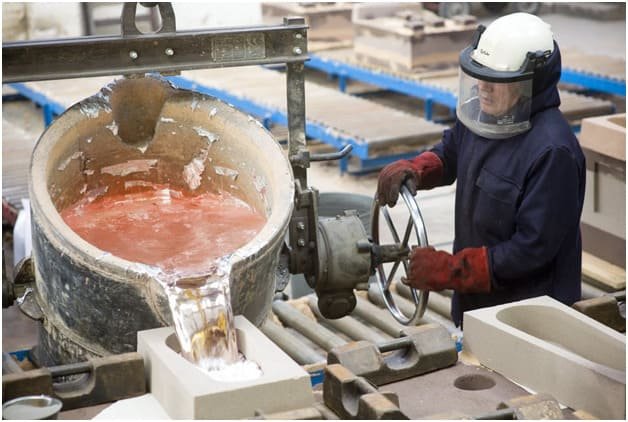

It consists of injecting a liquid metal contained in a container (die casting chamber) into the cavity of a cast iron casting made of steel, by means of a piston. In the first stage, air is eliminated from the die casting chamber. Then there is a quick filling of the permanent mold casting cavity to prevent the metal from cooling.
The last step is metal compaction to reduce the volume of microporosities resulting from the metal solidification contraction.
Tixo foundry
Also called semi-solid aluminum alloy foundry, but is already used on a large scale in developed countries such as Japan, the United States, Germany and Italy.
The technology uses, instead of liquid aluminum, metal in “paste”, avoiding wear in contact between the metal and the permanent mold casting and increasing productivity. The main applications of this process are in the automotive industry, in the manufacture of cast aluminum parts such as suspensions, housings and clutch discs, among others.
What is the technique of tixo die casting process?
The technique has been used since 1982 and one of its main advantages is less wear on the cast aluminum parts used in the process. As it is a 60% solid and 40% liquid material, semi-solid casting allows for less friction between the permanent mold casting and the metal, increasing its useful life and, consequently, productivity.
As a result, the cast material does not show porosity or segregation of alloying elements, offering a better quality result to the final product.
The Applications of tixo die casting project
Tixo Foundry is used in the production of components such as suspension support (rear and front), suspension trays, electronic die casting system housings, steering box, master cylinder housings, clutch disc, among others.
In a practical example, the use of the casting process of semi-solid aluminum alloys allows a part such as the engine support to have its weight reduced from 5 kg to 3 kg with the casting process.
There is almost no porosity and the repeatability is high. On the other hand, it has a high initial cost due to the need for a steel permanent mold casting for die casting. There are still usage restrictions on other die casting alloys.
Pressure die casting aluminum
In this last type of aluminum foundry, the metal alloy is poured by gravity and directly into a permanent mold casting with a press. Next, pressure is injected between 6 and 8 bar, still in liquid aluminum.
It is precisely the difference in pressure between the surface of the block and its center, in addition to the contact with the atmosphere, which “sends” all air residues and gaseous porosities to the surface of the blocks, thus guaranteeing a homogeneous and almost free material any porosity.
About the advantages, the main one is that it is possible to apply different types of metallic alloys. There is also a wide range of geometries that can be copied at low cost.
This happens because the method eliminates the use of expensive permanent mold castings or dies. As a disadvantage, we can point out the low repeatability and, possibly, the lack of homogeneity in large blocks, since their solidification is precocious.
Reasons to use aluminum castings
1. WEIGHT REDUCTION
The ICE high-speed train incorporates the latest technology, but the prototype was very heavy. The replacement of malleable iron and steel castings with cast aluminum resulted in a total weight reduction of 6.1 tonnes per train and at the same time reduced the load on the axle bearings of the two locomotives.
An example is the 196-kilogram split gearbox part, sand-cast with Alufont-52 (AICu4Ti) and artificially aged. It took the place of a 578-pound steel casing.
2. LOW MOMENT OF INERTIA
A low moment of inertia is an important requirement for aluminum die cast parts with linear or rotational movements and fast accelerations and decelerations, such as robots and high-speed conveying equipment.
Illustrated is a component of a high-speed press for forming automobile body plates. .

3. GOOD BALANCING
A thread support spool of a textile machine that guides thread at high speeds requires an extremely light construction with perfect balance. When made by deep drawing from sheet steel, the coil did not meet these requirements.
4. VIBRATION ABSORPTION
Metal-rubber joints of moving parts of a vehicle’s motor gear, which absorb vibrations from the road, have the bearing core made of aluminum, as they withstand the efforts. They replaced iron and substantially improved vibration absorption.
Due to the high compression forces and in view of the large volume required, these cores are made from Unifont-94 (AIZn10Si8Mg) and high pressure die cast. The alloy is self-aging and regains its original strength after vulcanization.
5. DUCTILITY
Ductile aluminum casting automatically reduces stress spikes produced by impact stress. An elevator control box subjected to a pulsating pressure of up to 400 bar, which was made from an iron casting, was replaced with a casting made in a permanent mold of Unifont-90 material (AIZn10Si8Mg).

7. DYNAMIC RESISTANCE
Aluminum castings are suitable for parts that are subject to tensile vibration stresses. For this reason, all steel load-carrying aluminum die cast parts on rail cars can be replaced with aluminum castings. A locomotive, branded as Aludrive (aluminium-powered), contains 750 kilos of aluminum castings, saving 500 kilos in weight.
Cast aluminum Summary
Now that you know what the main aluminum casting processes are, it is important that you also know that all the works mentioned require silicon (Si) along with aluminum. This happens because the element ensures good flow quality for molten and liquid aluminum, thus allowing filling.
There is also the possibility of developing cast alloys with varying levels of magnesium die casting (Mg) and zinc (Zn), depending on the standard of mechanical strength and elongation required, especially in larger parts








