Introduction
There are several methods of manufacturing aluminium. These are green sand, permanent molding and die casting. However, of all these methods, aluminium die casting is one of the most preferred and famous methods.
We would consider in detail the meaning of aluminium die casting, step-by-step production processes of aluminium die casting, the die casting machines and some notables in aluminium die casting processes. We would also consider the hallmarks of aluminium die casting, the industries served by aluminium die casting and its market trends.

Meaning of Aluminum Die Casting
Aluminium die casting is an automated casting process whereby aluminium alloy is pressed into a mold under high pressure and at a high speed. It’s a method of heating up aluminium alloys to a high temperature till they are molten. Here, there’s an injection of liquid aluminium under high pressure into a mold.
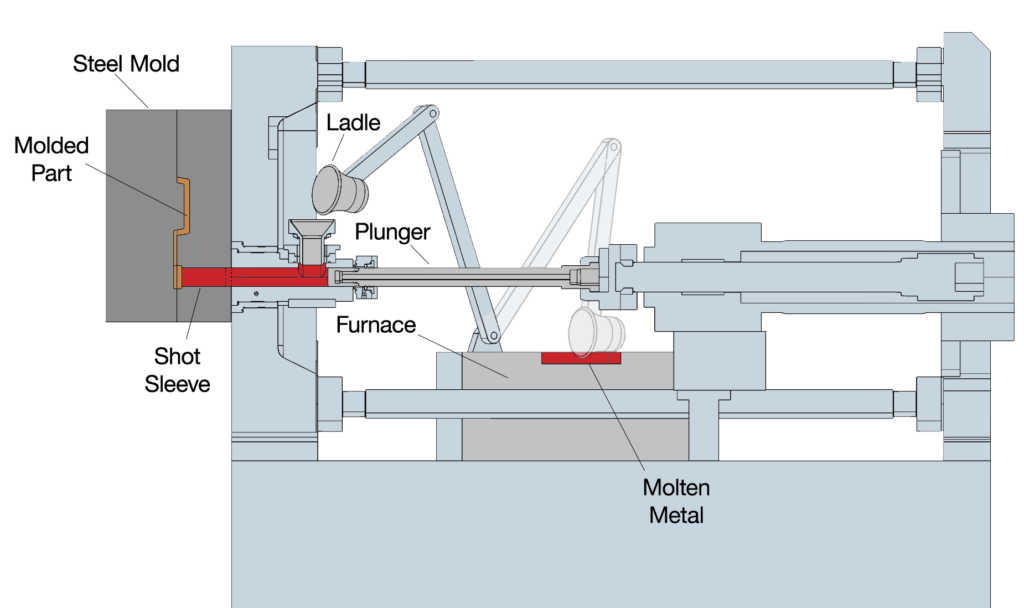
The mold consists of two halves separated to reveal the cast aluminium parts after the molten aluminium has solidified. One of the two halves is static while the other is mobile.

This results in aluminium products with a precisely formed and smooth surface. A single mold can be used multiple times and this makes aluminium die casting preferable for bulk productions.
Put differently, aluminium die casting refers to a manufacturing process of producing fine-textured and accurately designed aluminium parts through the use of reusable molds.
The aluminium alloys are heated in a furnace and then injected into the dies through the die casting machine. After cooling off, the material would retain the shape of the inner cavity of the mold and you can then remove it for further processing.
To do this, you would need aluminium alloy, furnace, die and a die casting machine. Of course, there may be the need for further secondary processes but this is always minimal. The production processes here are not too cumbersome, and so ultimately reduces the manufacturing cost. It also gives room for large production of die casting parts.

Aluminium is one of the most common metals. In fact, it occupies 80% of the Earth’s crust, thereby making it the most abundant metal. The most common aluminium include zinc, magnesium, copper, etc.
Aluminium die casting is preferable for speedy production of bulk metallic parts requiring minimal post-production machining. It produces high quality and reliable die casting parts. The production processes are also seamless as it requires minimal assembling. You can also integrate all the assembly features such as bosses, holes, students, etc. into the mold design at a go.
Using aluminium die casting, you can manufacture several parts such as cylinder beds, pistons, automotive connections, rods, electronic enclosures, plumbing, fittings, etc. Aluminium die casting enhances good mechanical properties.

You should note that die casting usually requires high volume production processes. It requires a special type of casting machine that’s quite expensive. So, to minimize the cost of production, die-cast parts are usually made in bulk productions. It may be difficult to get die cast prototypes and low-volume productions. This is because it is not in the best economic interest of the die casting manufacturer.
Aluminium die casting is an effective, seamless and cost-effective process offering a broader range of shapes and components than any other manufacturing technique. It offers decorative, impressive, trimmed and finished die-cast parts.
It offers monolithic die cast products. The different parts are wielded and this gives it strong material strength and quality.
Step-by-step Guide on the Production Processes of Aluminum Die Casting
Producing aluminium die-cast parts requires some procedures. Although the processes may theoretically appear tedious, it practically takes less than a minute. The procedures are:

(1.) You would have to prepare and clamp the two halves of the die. You would also need to clean the previous injection in each of the halves and then lubricate them to enhance the ejection of the next part. There is no particular number of times you must lubricate. This depends on the number of cavities and side cores.
However, note that the lubrication time increases with the pot size. Also, depending on the material you’re using, you may have to lubricate after every 2 or 3 cycles. Thereafter, you would close and clamp the two die halves attached inside the die casting machine together.
Note also that the clamping period depends on the type of machine you’re using. If you’re using a small machine, the clamping period would be shorter than that of a larger machine.

(2.) After this, you would move the molten metal into a chamber where it can be injected into the die. There are different ways of transferring a molten metal, depending on whether you’re using a hot chamber or cold chamber die casting machine. In the hot chamber, you can easily transfer the molten metal than in a cold chamber.
Thereafter, you would inject the molten metal at high pressure into the die. Usually, the pressure ranges between 1,000 to 20,0009 ps. During solidification, this pressure holds the molten metal in the dies. The whole injection period is really short, typically around 0.1 seconds.
To determine the injection time, you can check out the wall thickness of the casting and the thermodynamics properties of the material. A casting with a great wall thickness requires more injection time.

(3.) You should then expect the injected molten metal to begin cooling off. The molten metal will solidify when it enters the die cavity. When the cavity is filled and the molten metal solidifies, then the final shape of the casting is formed.
You can’t open the die until the cooling time had elapsed and the casting is solidified. You can predict the cooling time by the wall thickness of the casting. A thicker wall will require larger period to cool off. Also, a highly geometrically complex die may require a larger cooling time.

(4.) After cooling off, you can open the halves and push the casting out of the die cavity. The ejection mechanism must apply some force to eject the part. This is because, during cooling, some parts would have shrunk and adhered to the die.
(5.) When cooling off, you can peel off the excess materials in the channels of the die that is firmly attached to the casting. You can do this with a trimming press or by manually sawing or cutting them.
You should take note of the aluminium you would be using as this may affect the strength of the die-cast products. If you put the temperature of the die-cast machine at up to 212°, you will get a die-cast product with a tensile strength of 45Ks. Conversely, if you reduce the temperature to 75°, you will get a die-cast product of 24 KS.

Aluminium Die Castings and Die Casting Machines
There are two different types of die casting machines:
(1.) Hot Chamber Die Casting Machine: With this machine, the liquid aluminium alloy is in constant contact with the casting chamber and the melt passes through a valve into the casting chamber. It is mostly used for alloys with low melting points such as tin, zinc, lead, among others. This is not the procedure commonly used for aluminium die casting.
The hot chamber die casting is otherwise known as gooseneck machine. You would have to place the metal into a furnace and then melt the metal. Thereafter, the machine lifts the piston or plunger so the molten metal can enter the cylinder through the intake port.
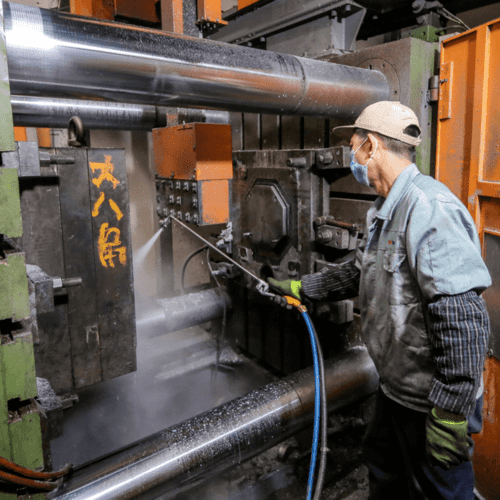

This then pushes the plunger downwards so the melted metal can touch the nozzle. You should keep pressing the plunger till the die cavity fills up with the liquid metal. You need to be patient for the liquid metal to solidify inside the cavity before using the ejector pin to eject the solid part and begin post-processing.
The cylinder chamber of the injecting mechanism is immersed in the molten metal bath. Then, a gooseneck metal feed system draws the molten metal into the die cavity. Although the direct immersion in the molten causes swift and convenient mold injection, it also causes increased corrosion susceptibility.
The typical injection pressures for hot-chamber die casting machines are between 1000 and 5000 ps.
The hot chamber die casting machine has a high degree of automation and production efficiency. However, it’s not commonly used in aluminium die casting. This is because it has a high melting point and the machine’s furnace can’t perfectly contain the heat to melt the aluminium alloys. Any attempt to use the hot chamber die casting power here may damage the machine parts or the furnace.

(2.) Cold Chamber Die Casting Machine: This procedure is common for casting materials with higher melting points and corrosive properties such as aluminium, copper, etc. First, you need to fill the alloy into the casting chamber and then pressed it into the die casting mold through channels.
Thereafter, the components solidify under strong pressure and you can then remove the patches of the mold. The automatically operated ejection pins remove the gate from the mold. Note that though these processes appear cumbersome, you can do it in a jiffy.

The cold chamber die casting machine is the most common and preferred for aluminium die casting. It can easily produce denser metal castings at a go. You would need to first heat the aluminium alloy in a different furnace and then move it to the casting machine. The machine forces the molten metal into the cavity of the mold by using a pressurised plunger.
Here, the procedures for die casting require that you ladle the molten metal from the furnace of the shot chamber using a pouring hole. The plunger will then force the metal through the sheet chamber into the die.
The cold chamber machine allows the integral fastening elements in the die-cast products. It also allows for complex shapes within closer tolerances than many other mass-production methods. The cold chamber die-cast parts are stronger and have thinner parts walls with enhanced mechanical properties.

This procedure requires that the molten aluminium alloy material is added to the die sheet from another separate origin. This makes the cold box casting machine function at a low temperature. Particularly, to use the cold chamber die casting machine:
(i) You would have to liquefy molten aluminium through a furnace.
(ii) You would then ladle the molten aluminium into the cold die-cast chamber.
(iii) Plunger forces the aluminium into the cavity under high or low pressure. This would cause the die to open.
(iv) The ejector would then force the die-cast part out of the ejector die, which causes the plunger to retract
The typical injection pressures here are between 2000 and 20000 ps.

Notables in Aluminum Die Casting Production Processes
(1.) The mold should be separated into two halves by a parting line. The parting line serves as the border between the internal and external parts. The parting line should be properly placed and the location where it would be placed should be designed at the early stage of production.
The designer and engineer should collaboratively consider the proper location for the parting line. It should also be positioned to allow the seamless flow of metals as this would increase the overall quality of the aluminium die-cast product.
If the molten metal would solidify before reaching every crevice in the die, you can design it with diverse injection points.

(2.) When the molten metal begins to cool off from melting temperature to room temperature, the casting will begin to shrink usually within a volume of 0.4-0.6%. This can lead to difficulty in ejection by constricting internal protrusions on the mold. To avoid any shrinkage, you can use drafting.
Draft refers to the small taper around the sides of the mold. This makes injection easy. You have to include the draft in all parallel surfaces of the die to ensure a seamless injection.
The importance of drafting in aluminium die casting is that it makes the aluminium casting seamless. The amount of draft needed depends on the designs. For inner holes and walls, you would need a larger draft while for outside walls, you would need a small draft.
Also, sometimes, aluminium can crack in shrink at high temperatures. You can alternatively combine silicone or copper with it. A combination of aluminium with silicone or copper would add to the fluidity and hardness of the aluminium.

(3.) For wall designing, don’t make the wall thin or appear feeble. A thin wall would affect the free flow of the molten metal. It would cause the metal to solidify when the mold is not yet filled up. You should ensure the wall is quite thick.
However, the wall should not be excessively thick because this may lead to resource wastage and increase in solidification time. Also, the wall thickness should be uniform, otherwise, the metal would not flow easily and hamper the solidification process.
(4.) Sharp edges are not advisable in aluminium die casting because they eventually reduce the strength of the cast components.

Create curved junctures between two surfaces of sharped edge. These curved junctures are the fillets and radii. The fillet is the curved juncture in the internal edges while the radi is the curved juncture in the external edges of the part. These rounded edges make it easier for injection of metals.
(5.) There are several types of aluminium alloys such as the A413, A380, A360, 383, CC401, B390, etc. These alloys have high electrical conductivity and excellent machining characteristics. They also have excellent castability, tool life and are easily recyclable.
However, you should not randomly pick any alloy without considering what you intend to use the die-cast product for. For the production of automotive engine blocks, consider using the B390. This is very durable, wear-resistant, hard and also has low ductility.
Alloy 380 is your go-to when you have no specification at heart. It’s versatile and you can use it for several productions. This is the most commonly used aluminium alloy. It is lightweight, resistant to hot cracking and corrosion.
(6.) To ensure the durability of your aluminium casting mold, you can apply head treatment and die coatings. This will slow down the heat checking and extend the tooling life span.

(7.) One of the preliminary stages of aluminium die casting is the die-designing stage. As a die designer, you should ensure the molten metal flow easily into all the cavities. The die design should also accommodate any complex features on the part.
In designing, also ensure there’s no excessive wall thickness and the wall thickness should be uniform.
Hallmarks of Aluminum Die Casting
There are several hallmarks of aluminium die casting that make it preferable among other aluminium die casting methods :
(1.) Aluminium die casting is the perfect go-to for creating products with complex designs and shapes. Die casting can create almost any geometry, lustre or surface texture. You can easily customize your designs.
There are some automated parts such as the engine blocks that require complex shapes that even machining can’t accurately create. This is where aluminium die casting comes in. No matter how complex the shapes are, die casting would perfectly produce them.
(2.) Aluminium die casting produces fine, finished and smooth surface. Its outputs are aesthetically pleasing. The reality is that aluminium die casting requires no machining or little machining and finishing.
It only needs machining when there’s a noticeable imperfection on it. If after producing the aluminium die-cast product, it has any rough surfaces, you can easily remedy this by sandblasting, sanding, etc. You can also apply a powder coat or any other decorative coat to the finished parts.
(3.) What if we told you that overall, aluminium die casting is more cost-effective than other ways of making aluminium? Yes, it is! Although other methods such as permanent molds and green sands may appear cheaper, they are however not as durable as aluminium die casting.
The permanent mold castings require the gravity pouring of molten aluminium into the mold, while green sand processes uses only wet sand to create the mold. These simplistic processes make them cheaper. However, aluminium die casting has better finished surface and tolerance level which makes it durable.
You can repeatedly use a cast to create several identical parts and this reduces the cost of production.
(4.) Of all metals, aluminium is often preferred for die casting because of its versatility, high dimensional stability, among others. In fact, aluminium is the most common metal for die casting.
(5.) Aluminium offers maximum durability and yet is lightweight. You can easily create very lightweight castings without compromising the quality and strength of your castings. Aluminium has a specific mass of 2700kg/m³.
Cooper and brass have a triple of this density.
(6.) Aluminium is also durable and resistant to corrosion. In the electrical and electronics industry, aluminium is the perfect go-to because of its high electrical/thermal conductivity.
(7.) Aluminium die casting can easily create intricate 3D designs at cost-effective prices. Unlike sheet metal forming and machining, it requires little or no finishings because it can turn molten metal into near-net-shape parts easily.
(8.) It allows for large production of castings within a jiffy. You don’t need to destroy a mold after making it and you can repeatedly use it to replicate similar designs. The mold consists of high-quality steel grades. Although it’s difficult and expensive to make, you can easily use a mold to create millions of castings.
Industries Served By Aluminium Die Casting
(1.) In the medical sector, there is a need for aluminium die castings to produce hospital beds, diagnostics equipment, ultrasound system, etc.
(2.) In the Industrial sector, aluminium die castings are used to manufacture industrial machinery.
(3.) In the military sector, aluminium die castings are used in producing ammunition. Examples of aluminium die-cast gun parts are the trigger guards, Remington receivers, among others.
(4.) In the renewable energy sector, aluminium die castings are used in the production of power generation and distribution components such as solar panel brackets, wind turbine parts, etc.

(5.) In the aerospace sector, aluminium die castings are also used.
(6.) They are commonly used in the automotive sector to manufacture lightweight and durable parts. Aluminium castings improves fuel efficiency by contributing to weight-saving requirement. It’s used to produce the rack housing, chain cover, etc.
(7.) In the telecommunications industry, aluminium die castings are used to provide EMI/RFU shielding, rigidity and durability.
(8.) In the power sector, aluminium die casts are used to create cylinder head, cover, cylinder block, crankcase, piston, pump body, pump cover, generator housing, engine gear chamber, etc.
(9.) In the electronic industry, you can use it in the production of connectors, enclosures, etc.
(10.) In the construction industry, you can also use aluminium die casting for large structures such as window frames and building frames.

General Overview of Aluminum Die Casting Market Trends
By 2022, the aluminium die casting market is projected to grow to 59.89 US Dollars at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.08%. By 2026, the market is projected to reach 82.58 US Dollars at a CAGR of 8.36%.
Regionally, the Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the aluminium die casting market. This is credited to several reasons, including the increasing demand and production of automobiles. For a fact, over half of the entire components in automotive vehicles are made of aluminium die-cast parts.
Globally, China is the largest manufacturer of die-cast parts with 51.95 million metric tons. This is almost half of the world’s production rate. With a production capacity of 11.31 million metric tons, India is the second-largest producer of die-cast products.

The Indian automotive parts aluminium die casting market is projected to register a CAGR of over 88%. India has state-friendly policies toward the aluminium die casting sector. Here, the government promotes foreign investments in the automobile industry by allowing 100% foreign direct investment.
The largest target market for aluminium die-cast parts is the automotive industry. Aluminium die casting is used in the structural components of high-quality new energy cars, chassis, towers, shock absorbers, etc.
As a result of the standards put in place by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers and American National Standards Institutes, the US die casting market has the highest standards globally.
Conclusion
Although there are several metals, aluminium is widely used in die casting. Also, there are different methods to manufacture aluminium. However, the die casting method is preferable for various reasons such as its ability to create complex designs.
In this article, we have explained the aluminium die casting in detail. This knowledge will always come in handy for you when faced with any issue of aluminium die casting.








