What is die casting?
In die casting, non-ferrous metals are melted and forced into a mold under pressure. Because it uses a mold, it is suitable for mass production. Unlike other castings, die casting is characterized by high dimensional accuracy due to the application of pressure. Also, since a mold is used instead of a sand mold, the surface is smooth.

Die Casting Alloys
Die casting is suitable for making complex shapes that cannot be processed with sheet metal, or for making products that do not have sufficient strength with resin. Because it can create complex three-dimensional shapes, it offers a higher degree of freedom than sheet metal processing, and has a higher yield rate than cutting.
On the other hand, pipes and hollow shapes cannot be created. Also, since we use a mold, we are not very good at creating under shapes that protrude inwards like overhangs, or shapes such as holes on the sides.

Materials such as aluminum alloys, zinc alloys, magnesium alloys, and copper are used for die casting. In particular, hot chamber die casting and zinc die casting are often used. On the drawings, aluminum die-casting is indicated as ADC, and zinc die-casting as ZDC.
Features of hot chamber die casting and zinc die casting
Aluminum die-casting is very light, stronger than zinc die-casting, and has little dimensional change over time. Therefore, it is used in many parts such as automobile transmission cases. It is also used for cases that also serve as heat sinks, taking advantage of its good thermal conductivity.
Zinc die casting, on the other hand, is heavier and less strong than high pressure die casting. However, it is highly machinable and can produce more complex and precise parts than high pressure die casting. It is used to manufacture finely shaped parts that do not require much strength.
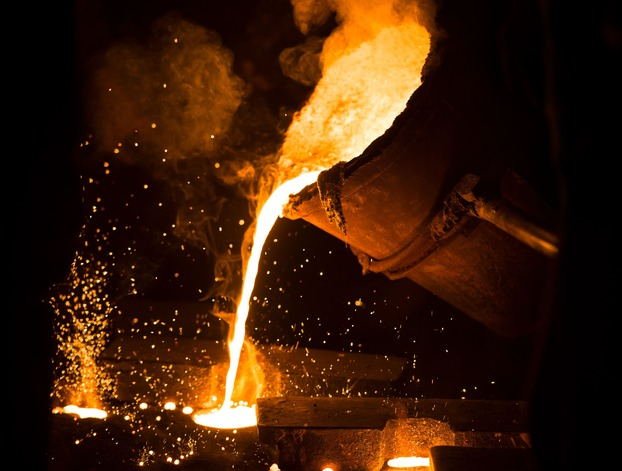

It is also often used in automobile parts and industrial machine structures. It is also used for furniture handles because of its easy surface treatment.
Although the dimensional accuracy of die-cast products is high for casting, it is not very high compared to machining. For this reason, in many cases, the mating surfaces of die-cast products, mounting parts for other parts, fastening surfaces for screws, etc. are machined before assembly.
Precautions when using die casting
Die casting excels in mass production and makes it easy to create complex shapes, but it also has its disadvantages.
Disadvantages of die casting include:
When molten metal is poured under pressure, air is entrapped. Even with the same aluminum and zinc materials, the strength is lower than that of parts made by cutting. I have a problem going down. There is also a method of pouring metal into the mold while it is in a vacuum state, but it requires a lot of cost to improve it perfectly.
The initial cost is high
Die casting requires a mold. In addition, since it is necessary to pour molten metal, the production equipment becomes quite expensive. Therefore, if there is no prospect of mass-producing a large number of products like automobiles, there is a possibility that the cost will not be recovered.
The molten metal processing industry plays a very important role in the development of the economy. In sectors such as automotive, medicine, aviation or the electrotechnical and electronic industry, molten metal elements are being introduced as an innovation.
This is due to the dynamic development of their processing technology. Each production of molten metals aims to strive for the best quality of products at the lowest possible production costs. The most commonly used method is molten metal injection.
The greatest advantages of the production of injection molds are the very high repeatability of products and the possibility of producing elements with a complicated structure, often unattainable with other manufacturing methods.
Die casting processes
Injection is a cyclical process consisting of the following steps:
1. Mold closure,
The mold assembly (1) attached to the movable table (2) of the hot chamber die casting machine is moved along the guides by means of the hydraulic system (10) towards the mold (3) fixed to the stationary table
Scheme of the high pressure die casting machine
2. Access of the injection unit to the matrix
The injection nozzle (8) is moved to the injection sleeve (9) of the mold using the hydraulic system (10) of the screw (11). As a result of this action, the liquid material is squeezed into the cavity (12) of the mold.
3. Filling the mold cavity with liquefied material,
The rotational movement of the screw causes the material to be taken from the hopper (14) in the amount required for injection and its strong mixing. The combination of high pressure generated by the screw in the cylinder of the die casting process machine and high temperature causes the metal casting to liquefy, which fills the mold cavities during injection.
d) Pressure,
e) investment casting of the material,
f) cooling of the forming surfaces,
g) removal of the unit,
h) opening of the mold and removal of the molding
Construction of the die casting process machine
Die casting process machines are used to produce details of various colors, shapes and sizes from various low melting points. Types of low melting points are described in the article Low melting points. The figure below shows the construction of a traditional die casting process machine.
1. Closing unit.
2. Control panel with indicators.
3. Sand casting unit.
4. Injection unit.
5. Machine bed.
Injection unit
The injection unit is the most important part of the cold chamber die casting alloys responsible for preparing the metal casting for injection into the mold. The main function of this element of the machine is the homogeneous melting of the material.
Construction of the injection unit
Construction of the injection unit
1. Screw cylinder.
2. Displacement cylinder.
3. Tension wedge.
4. Worm clutch.
5. Injection piston.
6. Drive shaft.
7. Drive motor.
8. Precision linear guides.
9. Column support.
Sand casting unit
The material fed through the loading hopper is transported by the rotating auger. As the material moves forward due to the rotation of the screw, the material is in contact with the hot wall of the cylinder. In addition, due to the rotation (shearing of the molded mass), additional heat (frictional heat) is generated.
With the increasing degree of filling of the screw vestibule, the mass transported to it moves the screw back more and more, until the set displacement of investment casting is reached. The low melting pointed mass can then be injected into the mold cavity by the non-rotating screw, which now acts as a piston. While the molded mass is cooling in the mold, the material can be low melting pointed for the next injection.
Construction of the sand casting unit
1. Nozzle.
2. Cylinder head.
3. Thermal sensor.
4. Feed opening.
5. SC flange
6. Heating tapes.
3-zone auger
Types of snails
Standard auger
Universal auger for processing various materials. Optimum performance cannot always be achieved with this auger, but in many cases, it meets the requirements.

Mixing auger
For the addition (mechanical homogenization) of color pigments and powder granules, as well as for the direct processing of several components into a paste, i.e. for the homogenization of materials with different viscosities and different molecular weight distributions. It is used with particularly high requirements regarding the mechanical and thermal homogeneity of the molded mass.
Special snails
Special screws take into account the special thermal, rheological, and tribological properties of special materials. (PVC, durolow melting points, elastomers)
Screw with degassing
Processing of all absorbent materials that for optical or technological reasons must be dried before processing, in particular for the processing of reclaimed absorbent materials.
High-performance auger (HP: HIGH PERFORMANCE)
Increased sand casting efficiency, means reducing sand casting time or cycle time while maintaining or even increasing the quality of the melt.
Better homogeneity of the melt, means that the melt has a very high level of homogeneity both mechanically and thermally.
Optimum dyeing, good mixing performance due to the combination of mixing elements and shear gaps allows dyeing with significantly lower proportions of coloring agents and guarantees an extremely uniform distribution of the dye.
Increased productivity
The general tendency to shorten cycles by improving the technical solutions of molds or increasing the number of cavities increases the demands placed on screws with regard to sand casting performance. The HP high-performance screw ensures that sand casting does not increase cycle time in high throughput applications.
Lower machine costs
Thanks to the high efficiency of the HP screw, it is possible to use a smaller injection unit in many cases.
Less energy consumption
The effects described above are obtained with the same machine setting. This means that thanks to increased production capacity and shorter cycle times, the energy consumption per part is reduced.
The larger scope of the application
Unlike the screws with separated zones (barrier zones), the HP High-Performance Screw offers the user a much wider range of applications. It is characterized by high rigidity of transport and guarantees, even with large screw pitches (>3D), optimal melting of the material with constant transport efficiency.
At the time of investment casting of the material, the material is injected into the injection mold, where the specific shape of the molding is mapped. The construction of a typical injection mold is discussed in the article e:

A very important parameter in the cold chamber die casting process is the correct temperature of the injection mold cavity. This factor significantly affects the final quality of the element and the time of the entire cycle.
Literature shows that mold cooling time accounts for 80% of the entire injection cycle. The molds are cooled with water, often enriched with agents that improve its properties. In each form of cooling zones receiving heat flows are separated by individual cooling channels.
Mostly zones are separated:
– cooling of molding forming surfaces,
– mold body cooling,
– injection nozzle cooling,
– cooling areas of hot-runner systems,
– cooling of cores and mold sliders.
Before each removal of the mold from the cold chamber die casting alloys, the cooling circuits must be emptied of water and then dried. During inspections of molds, it is necessary to check the patency and tightness of the cooling circuits. More details related to mold inspections are discussed in article 5.3 Injection Mold Operation, where the main principles of maintenance are discussed.
When the cycle of pushing and removing the part from the mold is completed, the finished part is collected and put away in the designated place. This can be done with the help of a human, gravitational fall, and new technologies can be used.
Cold Chamber Die Casting
A very common solution on the market regarding the automatic operation of cold chamber die casting machines are the use of linear robots placed above the injection mold. The task of this device is a precise and quick collection of moldings.
They are dynamic and precise. The robot picks up parts in less than one second with a repeatability of ±0.1 mm. The versatility of these devices allows them to be adapted to various models of hot chamber die casting machines.
However, the robot must need an appropriate gripping tool, in the case of molded parts, these are grippers that will enable them to be gripped. Depending on the shape and surface of the part, grippers of various construction are used.
Casting Process and Functions
The most important functions of this part are the secure grip of the molding and its gating system, holding the object during the operation, and releasing it at the target place. There is a whole range of standardized gripping tips, suction cups, or shears on the market, which will allow you to design the gripper to the needs of the manufactured part.

Appropriate setting of this process will allow for the production, where the only human task will be to control the quality of the manufactured product.
In the production of low melting point elements, gripping by suction is most often used, because molded parts are thin and relatively light products.
Aluminum alloy starting from ADC is a casting made by die casting method. Aluminum is melted into a liquid, and molten metal is poured into a mold at high speed for molding. These are called high pressure die castings or aluminum alloy die castings.
Features of high pressure die casting
Die casting requires molten metal to be injected at a higher speed than normal casting, so the molten aluminum must also have high fluidity. For this reason, the chemical composition is slightly different from other aluminum castings.
For example, Fe, which is added for aluminum alloy die casting, is an impurity in the base metal for ordinary aluminum casting, but in the case of aluminum die casting, it is intentionally added, and this prevents the mold from seizing. It is for prevention.
Casting is said to be difficult to achieve precision, but one of the major features of die casting services is its ability to achieve high dimensional precision, making it a production method particularly suitable for mass production.
Heat treatment of die casting services
Most metal materials are heat-treated for practical use, but in the case of die casting services, the finished casting is often not heat-treated. In some cases, this is said to be because it may expand due to heat treatment and cause internal defects. The lack of a heat treatment process also shortens the production cycle.
However, in recent years, the demand for higher quality aluminum castings and technological innovation to meet them have progressed, and among the die casting methods, a method called a special die casting method is becoming widespread.

This method includes the vacuum die casting method and the non-porous die casting method, and when using these methods, heat treatment (T6 heat treatment) is possible. In this case, as with other metals, heat treatment improves mechanical and physical properties.
Due to the improvement in mechanical properties, which was one of the weak points of aluminum castings that are strong against mass production, the applications are expanding.
Molds used in die casting services
The reason why mass production of die casting is possible is that it uses a mold that can be used repeatedly, that molten metal can be poured at high speed by applying pressure, and that the molten metal solidifies faster than other casting methods due to rapid solidification.
There are things you can do. For this reason, the molds are expensive, but it is customary to use high-precision molds made of heat-resistant steel that can be used repeatedly.
Effects of impurities contained in aluminum ingots
In the die casting method, the melted metal cools quickly, so it solidifies quickly (rapid solidification). It also has the advantage of having less impact. Due to this characteristic, it is possible to use recycled ingots as the base metals, which is very cost-effective.
In addition, rapid solidification is characterized by a finer metallographic structure than other casting solidifications, which helps improve mechanical properties. Another advantage is that the surface looks good despite the high speed casting.
Disadvantages of die casting
On the other hand, the disadvantage of using aluminum die-casting is that it is more difficult to manufacture when using it for large items, thick items, and high-strength components. This can be said to be the fate of castings.
Among aluminum die-casts, some are relatively strong, but compared to other metal-based materials that emphasize strength, many of them are not suitable for applications where strong loads are continuously applied.
Another problem in manufacturing is that the molten metal does not flow into the corners of the mold because the molten metal is injected at high speed.
The aluminum die casting process
Since aluminum (molten metal) melted under pressure is injected into the mold, air may be trapped inside the product, creating a “hole” inside the product. This is also known as a blowhole (chair), and there are two main types depending on the cause. “
In order to maintain castability and consider the thermal shock and heat load on the mold, it is not suitable for metals and alloys with high melting points. and magnesium, copper, lead, and tin.

Brass is said to be the limit for applicable metals, and the die casting method is said to be difficult for metals with melting points higher than this. Although aluminum has a lower melting point than other metals such as steel, it has a high melting point among metals that use the die casting method.
Die-casting of high-melting-point copper alloys, etc., also poses the problem of increased production costs because the life of the mold is rapidly reduced.
Highly manufacturable method
For production, we use a continuous casting machine called magnesium die casting alloys for mass production.
Conversely, the cost of a single item is high, but because it is possible to shorten the process from metal to product and recycle it, it is a standard material that is very often used especially around engines and housings in the automobile industry. Among the casting technologies suitable for mass production, it has outstanding mass productivity.
Die casting services standards and requirements
In terms of standards, in addition to the existing JIS, symbols ported from ISO have been added since 2006.
In addition to mechanical properties, and physical and chemical properties, when making a selection, it is important to consider castability and workability, which greatly affect production, base metal cost (whether or not recycled metal is used), and surface Ease of processing is also an item to consider.
The requirements for aluminum die-cast materials are also slightly different from those of other metallic materials, and this property, also called die-castability, mainly determine the quality of castability. Small solidification shrinkage, no sticking to the mold, excellent pressure resistance, less likely to cause casting cracks and shrinkage cavities, good fluidity and excellent cavity filling, etc..
summary
In die casting, aluminum die casting and zinc die casting are mainly used. Aluminum die-casting is light, durable, and has the characteristic of being a good conductor of heat. Zinc die casting is characterized by good workability and high dimensional accuracy. Let’s make use of each feature and select the processing method.
What is die casting?
In die casting, non-ferrous metals are melted and forced into a mold under pressure. Because it uses a mold, it is suitable for mass production. Unlike other castings, die casting is characterized by high dimensional accuracy due to the application of pressure. Also, since a mold is used instead of a sand mold, the surface is smooth.
Die Casting Alloys
Die casting is suitable for making complex shapes that cannot be processed with sheet metal, or for making products that do not have sufficient strength with resin. Because it can create complex three-dimensional shapes, it offers a higher degree of freedom than sheet metal processing, and has a higher yield rate than cutting.
On the other hand, pipes and hollow shapes cannot be created. Also, since we use a mold, we are not very good at creating under shapes that protrude inwards like overhangs, or shapes such as holes on the sides.
Materials such as aluminum alloys, zinc alloys, magnesium alloys, and copper are used for die casting. In particular, hot chamber die casting and zinc die casting are often used. On the drawings, aluminum die-casting is indicated as ADC, and zinc die-casting as ZDC.
Features of hot chamber die casting and zinc die casting
Aluminum die-casting is very light, stronger than zinc die-casting, and has little dimensional change over time. Therefore, it is used in many parts such as automobile transmission cases. It is also used for cases that also serve as heat sinks, taking advantage of its good thermal conductivity.

Zinc die casting, on the other hand, is heavier and less strong than high pressure die casting. However, it is highly machinable and can produce more complex and precise parts than high pressure die casting. It is used to manufacture finely shaped parts that do not require much strength.
It is also often used in automobile parts and industrial machine structures. It is also used for furniture handles because of its easy surface treatment.
Although the dimensional accuracy of die-cast products is high for casting, it is not very high compared to machining. For this reason, in many cases, the mating surfaces of die-cast products, mounting parts for other parts, fastening surfaces for screws, etc. are machined before assembly.
Precautions when using die casting
Die casting excels in mass production and makes it easy to create complex shapes, but it also has its disadvantages.
Disadvantages of die casting include:
When molten metal is poured under pressure, air is entrapped. Even with the same aluminum and zinc materials, the strength is lower than that of parts made by cutting. I have a problem going down. There is also a method of pouring metal into the mold while it is in a vacuum state, but it requires a lot of cost to improve it perfectly.
The initial cost is high
Die casting requires a mold. In addition, since it is necessary to pour molten metal, the production equipment becomes quite expensive. Therefore, if there is no prospect of mass-producing a large number of products like automobiles, there is a possibility that the cost will not be recovered.

The molten metal processing industry plays a very important role in the development of the economy. In sectors such as automotive, medicine, aviation or the electrotechnical and electronic industry, molten metal elements are being introduced as an innovation.
This is due to the dynamic development of their processing technology. Each production of molten metals aims to strive for the best quality of products at the lowest possible production costs. The most commonly used method is molten metal injection.
The greatest advantages of the production of injection molds are the very high repeatability of products and the possibility of producing elements with a complicated structure, often unattainable with other manufacturing methods.
Die casting processes
Injection is a cyclical process consisting of the following steps:
1. Mold closure,
The mold assembly (1) attached to the movable table (2) of the hot chamber die casting machine is moved along the guides by means of the hydraulic system (10) towards the mold (3) fixed to the stationary table (4).
Scheme of the high pressure die casting machine
2. Access of the injection unit to the matrix
The injection nozzle (8) is moved to the injection sleeve (9) of the mold using the hydraulic system (10) of the screw (11). As a result of this action, the liquid material is squeezed into the cavity (12) of the mold.
3. Filling the mold cavity with liquefied material,
The rotational movement of the screw causes the material to be taken from the hopper (14) in the amount required for injection and its strong mixing. The combination of high pressure generated by the screw in the cylinder of the die casting process machine and high temperature causes the metal casting to liquefy, which fills the mold cavities during injection.
d) Pressure,
e) investment casting of the material,
f) cooling of the forming surfaces,
g) removal of the unit,
h) opening of the mold and removal of the molding
Construction of the die casting process machine
Die casting process machines are used to produce details of various colors, shapes and sizes from various low melting points. Types of low melting points are described in the article Low melting points. The figure below shows the construction of a traditional die casting process machine.
1. Closing unit.
2. Control panel with indicators.
3. Sand casting unit.
4. Injection unit.
5. Machine bed.
Injection unit
The injection unit is the most important part of the cold chamber die casting alloys responsible for preparing the metal casting for injection into the mold. The main function of this element of the machine is the homogeneous melting of the material.
Construction of the injection unit
Construction of the injection unit
1. Screw cylinder.
2. Displacement cylinder.
3. Tension wedge.
4. Worm clutch.
5. Injection piston.
6. Drive shaft.
7. Drive motor.
8. Precision linear guides.
9. Column support.
Sand casting unit
The material fed through the loading hopper is transported by the rotating auger. As the material moves forward due to the rotation of the screw, the material is in contact with the hot wall of the cylinder. In addition, due to the rotation (shearing of the molded mass), additional heat (frictional heat) is generated.
With the increasing degree of filling of the screw vestibule, the mass transported to it moves the screw back more and more, until the set displacement of investment casting is reached. The low melting pointed mass can then be injected into the mold cavity by the non-rotating screw, which now acts as a piston. While the molded mass is cooling in the mold, the material can be low melting pointed for the next injection.
Construction of the sand casting unit
1. Nozzle.
2. Cylinder head.
3. Thermal sensor.
4. Feed opening.
5. SC flange
6. Heating tapes.
3-zone auger
Types of snails
Standard auger
Universal auger for processing various materials. Optimum performance cannot always be achieved with this auger, but in many cases, it meets the requirements.

Mixing auger
For the addition (mechanical homogenization) of color pigments and powder granules, as well as for the direct processing of several components into a paste, i.e. for the homogenization of materials with different viscosities and different molecular weight distributions. It is used with particularly high requirements regarding the mechanical and thermal homogeneity of the molded mass.
Special snails
Special screws take into account the special thermal, rheological, and tribological properties of special materials. (PVC, durolow melting points, elastomers)
Screw with degassing
Processing of all absorbent materials that for optical or technological reasons must be dried before processing, in particular for the processing of reclaimed absorbent materials.
High-performance auger (HP: HIGH PERFORMANCE)
Increased sand casting efficiency, means reducing sand casting time or cycle time while maintaining or even increasing the quality of the melt.
Better homogeneity of the melt, means that the melt has a very high level of homogeneity both mechanically and thermally.
Optimum dyeing, good mixing performance due to the combination of mixing elements and shear gaps allows dyeing with significantly lower proportions of coloring agents and guarantees an extremely uniform distribution of the dye.
Increased productivity
The general tendency to shorten cycles by improving the technical solutions of molds or increasing the number of cavities increases the demands placed on screws with regard to sand casting performance. The HP high-performance screw ensures that sand casting does not increase cycle time in high throughput applications.
Lower machine costs
Thanks to the high efficiency of the HP screw, it is possible to use a smaller injection unit in many cases.
Less energy consumption
The effects described above are obtained with the same machine setting. This means that thanks to increased production capacity and shorter cycle times, the energy consumption per part is reduced.
The larger scope of the application
Unlike the screws with separated zones (barrier zones), the HP High-Performance Screw offers the user a much wider range of applications. It is characterized by high rigidity of transport and guarantees, even with large screw pitches (>3D), optimal melting of the material with constant transport efficiency.
At the time of investment casting of the material, the material is injected into the injection mold, where the specific shape of the molding is mapped. The construction of a typical injection mold is discussed in the article e:

A very important parameter in the cold chamber die casting process is the correct temperature of the injection mold cavity. This factor significantly affects the final quality of the element and the time of the entire cycle.
Literature shows that mold cooling time accounts for 80% of the entire injection cycle. The molds are cooled with water, often enriched with agents that improve its properties. In each form of cooling zones receiving heat flows are separated by individual cooling channels.
Mostly zones are separated:
– cooling of molding forming surfaces,
– mold body cooling,
– injection nozzle cooling,
– cooling areas of hot-runner systems,
– cooling of cores and mold sliders.
Before each removal of the mold from the cold chamber die casting alloys, the cooling circuits must be emptied of water and then dried. During inspections of molds, it is necessary to check the patency and tightness of the cooling circuits. More details related to mold inspections are discussed in article 5.3 Injection Mold Operation, where the main principles of maintenance are discussed.
When the cycle of pushing and removing the part from the mold is completed, the finished part is collected and put away in the designated place. This can be done with the help of a human, gravitational fall, and new technologies can be used.
Cold Chamber Die Casting
A very common solution on the market regarding the automatic operation of cold chamber die casting machines are the use of linear robots placed above the injection mold. The task of this device is a precise and quick collection of moldings.
They are dynamic and precise. The robot picks up parts in less than one second with a repeatability of ±0.1 mm. The versatility of these devices allows them to be adapted to various models of hot chamber die casting machines.
However, the robot must need an appropriate gripping tool, in the case of molded parts, these are grippers that will enable them to be gripped. Depending on the shape and surface of the part, grippers of various construction are used.
Casting Process and Functions
The most important functions of this part are the secure grip of the molding and its gating system, holding the object during the operation, and releasing it at the target place. There is a whole range of standardized gripping tips, suction cups, or shears on the market, which will allow you to design the gripper to the needs of the manufactured part.
Appropriate setting of this process will allow for the production, where the only human task will be to control the quality of the manufactured product.

In the production of low melting point elements, gripping by suction is most often used, because molded parts are thin and relatively light products.
Aluminum alloy starting from ADC is a casting made by die casting method. Aluminum is melted into a liquid, and molten metal is poured into a mold at high speed for molding. These are called high pressure die castings or aluminum alloy die castings.
Features of high pressure die casting
Die casting requires molten metal to be injected at a higher speed than normal casting, so the molten aluminum must also have high fluidity. For this reason, the chemical composition is slightly different from other aluminum castings.
For example, Fe, which is added for aluminum alloy die casting, is an impurity in the base metal for ordinary aluminum casting, but in the case of aluminum die casting, it is intentionally added, and this prevents the mold from seizing. It is for prevention.
Casting is said to be difficult to achieve precision, but one of the major features of die casting services is its ability to achieve high dimensional precision, making it a production method particularly suitable for mass production.
Heat treatment of die casting services
Most metal materials are heat-treated for practical use, but in the case of die casting services, the finished casting is often not heat-treated. In some cases, this is said to be because it may expand due to heat treatment and cause internal defects. The lack of a heat treatment process also shortens the production cycle.
However, in recent years, the demand for higher quality aluminum castings and technological innovation to meet them have progressed, and among the die casting methods, a method called a special die casting method is becoming widespread.

This method includes the vacuum die casting method and the non-porous die casting method, and when using these methods, heat treatment (T6 heat treatment) is possible. In this case, as with other metals, heat treatment improves mechanical and physical properties.
Due to the improvement in mechanical properties, which was one of the weak points of aluminum castings that are strong against mass production, the applications are expanding.
Molds used in die casting services
The reason why mass production of die casting is possible is that it uses a mold that can be used repeatedly, that molten metal can be poured at high speed by applying pressure, and that the molten metal solidifies faster than other casting methods due to rapid solidification.
There are things you can do. For this reason, the molds are expensive, but it is customary to use high-precision molds made of heat-resistant steel that can be used repeatedly.
Effects of impurities contained in aluminum ingots
In the die casting method, the melted metal cools quickly, so it solidifies quickly (rapid solidification). It also has the advantage of having less impact. Due to this characteristic, it is possible to use recycled ingots as the base metals, which is very cost-effective.
In addition, rapid solidification is characterized by a finer metallographic structure than other casting solidifications, which helps improve mechanical properties. Another advantage is that the surface looks good despite the high speed casting.
Disadvantages of die casting
On the other hand, the disadvantage of using aluminum die-casting is that it is more difficult to manufacture when using it for large items, thick items, and high-strength components. This can be said to be the fate of castings.
Among aluminum die-casts, some are relatively strong, but compared to other metal-based materials that emphasize strength, many of them are not suitable for applications where strong loads are continuously applied.
Another problem in manufacturing is that the molten metal does not flow into the corners of the mold because the molten metal is injected at high speed.
The aluminum die casting process
Since aluminum (molten metal) melted under pressure is injected into the mold, air may be trapped inside the product, creating a “hole” inside the product. This is also known as a blowhole (chair), and there are two main types depending on the cause. “
In order to maintain castability and consider the thermal shock and heat load on the mold, it is not suitable for metals and alloys with high melting points. and magnesium, copper, lead, and tin.
Brass is said to be the limit for applicable metals, and the die casting method is said to be difficult for metals with melting points higher than this. Although aluminum has a lower melting point than other metals such as steel, it has a high melting point among metals that use the die casting method.
Die-casting of high-melting-point copper alloys, etc., also poses the problem of increased production costs because the life of the mold is rapidly reduced.
Highly manufacturable method
For production, we use a continuous casting machine called magnesium die casting alloys for mass production.
Conversely, the cost of a single item is high, but because it is possible to shorten the process from metal to product and recycle it, it is a standard material that is very often used especially around engines and housings in the automobile industry. Among the casting technologies suitable for mass production, it has outstanding mass productivity.
Die casting services standards and requirements
In terms of standards, in addition to the existing JIS, symbols ported from ISO have been added since 2006.
In addition to mechanical properties, and physical and chemical properties, when making a selection, it is important to consider castability and workability, which greatly affect production, base metal cost (whether or not recycled metal is used), and surface Ease of processing is also an item to consider.
The requirements for aluminum die-cast materials are also slightly different from those of other metallic materials, and this property, also called die-castability, mainly determine the quality of castability. Small solidification shrinkage, no sticking to the mold, excellent pressure resistance, less likely to cause casting cracks and shrinkage cavities, good fluidity and excellent cavity filling, etc..
summary
In die casting, aluminum die casting and zinc die casting are mainly used. Aluminum die-casting is light, durable, and has the characteristic of being a good conductor of heat. Zinc die casting is characterized by good workability and high dimensional accuracy. Let’s make use of each feature and select the processing method.








