The die-casting sector mainly involves the use of zinc and aluminum alloys, which has increased in recent times. It is important to understand the distinctions between zinc and aluminum in order to choose the right material and maximize its use.
“Castingod is a Top Aluminum Die Casting Company in USA”
Zinc die-casting is the process of injecting molten zinc material into a mold and producing a product under pressure.
Similarly, aluminum die-casting is the process of injecting molten aluminum into a mold to produce a part under pressure.
Many industrial and commercial sectors use zinc and aluminum die-cast products like:
- Furniture pieces,
- Construction accessories,
- Automobile parts and other goods.
In this article, we will explore important characteristics of zinc and aluminum, their die-casting processes, and their popular applications.
What Are Aluminum and Zinc?

Aluminum and zinc are two distinct metals with distinctive properties. Zinc is a lightweight metal that is commonly used in:
- Die-casting
- Galvanizing steel
- Brass manufacture
Aluminum is a strong and lightweight metal that is used in many applications, like:
- Window frames
- Aircraft construction
- Beverage cans
What is Zinc Alloy?
Zinc alloy is a metal alloy largely made of zinc and other metallic elements. The most popular elements in zinc alloys are:
- Aluminum
- Magnesium
- Copper
- Cadmium
- Lead
- Titanium
The components of zinc alloys are melted and then processed to create the desired material shape using die-casting techniques.
They are used in a variety of industries, including die-casting for tools and auto components and hot-dip galvanizing for boiler water wall pipes to increase high-temperature corrosion resistance.
Properties of A Zinc Alloy
- It has outstanding casting performance, making it possible to produce complex, thin-walled precision pieces with a clean surface finish.
- It allows surface finishing options like electroplating, grinding, spraying, painting, and polishing.
- It resists pressure corrosion, doesn’t stick to molds, and doesn’t absorb iron die-casting processes.
- It provides wear resistance at room temperature and has good mechanical qualities.
- It features a low 385°C melting point, making die-casting simple.
What is Aluminum Alloy?
Alloys made of aluminum are referred to as aluminum alloys. It features a number of primary alloying components, including:
- Copper
- Silicon
- Magnesium
- Zinc
- Manganese, as well as secondary alloying components, including
- Nickel
- Iron
- Titanium
- Chromium
- Lithium
Aluminum alloy has a lower density than steel on a numerical scale. Additionally, in terms of strength, steel is stronger than aluminum.
It is a popular alloy across many sectors due to its outstanding versatility and plasticity. Its applications are widespread, like:
- The fields of aerospace
- Aviation
- Automobiles
- Equipment production
- Shipbuilding
- Chemicals
Properties of Aluminum Alloy

- Its light weight makes it perfect for sectors where weight reduction is important.
- Outstanding thermal conductivity.
- A composition that is environmentally friendly.
- Cold temperature resistance.
- The ability to use heat treatment to provide favorable mechanical properties, physical traits, and corrosion resistance
- High-strength qualities.
Aluminum Die-casting and Its Benefits
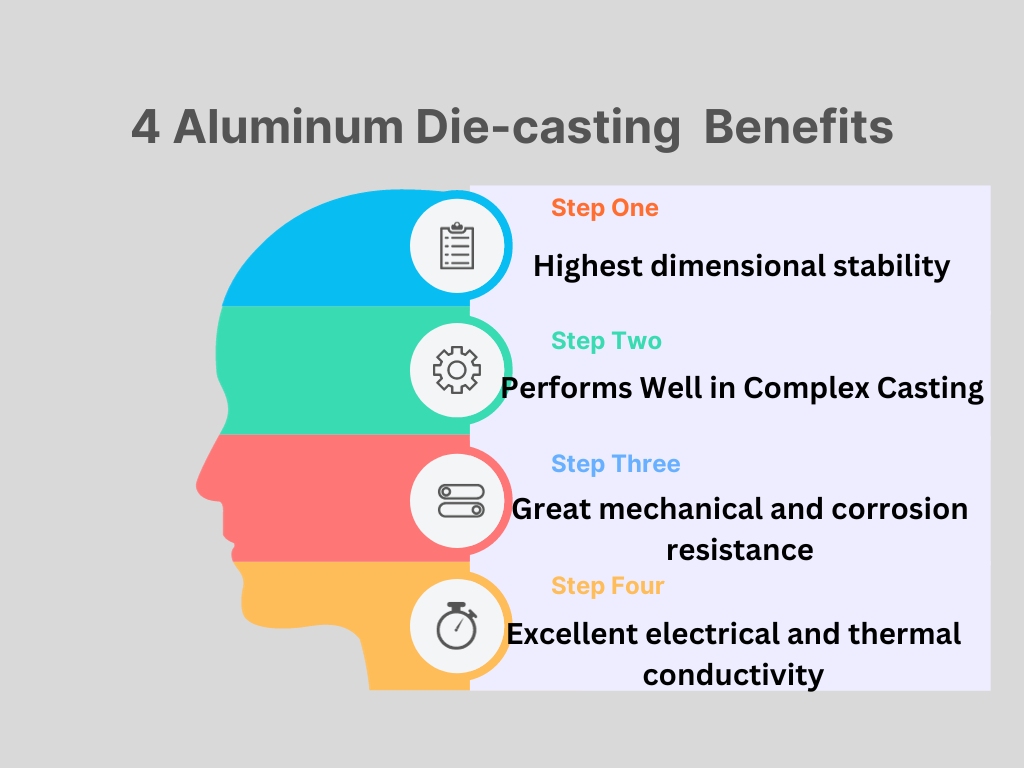
Die-casting aluminum alloys have the highest dimensional stability and are incredibly light. They perform particularly well for difficult geometrically intricate sections, such as small walls.
Aluminum alloys are the perfect alloy to use in die-casting because they have great mechanical and corrosion resistance as well as excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. Aluminum alloys are frequently used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Electronics
- Tools for hand and electric power
- Housings for lawnmowers
- Gear cases
- Lighting
- Communications equipment
Zinc Die-casting and Its Benefits
Zinc alloys are well known for their great flexibility, impact strength, and ability to be finished. Additionally, they have melting values that are lower than those of aluminum, which could contribute to a longer life. Due to these benefits, using this alloy requires less material than using other alloys, which helps users finish projects faster and cheaper.
Zinc is often used for the following auto parts:
- Interior decorative elements
- Additional engine parts
- Power steering systems
- Brake parts and systems
- Systems and components for air conditioning
- Fuel systems
- electronics
Difference Between Zinc and Aluminum Die-casting

The differences between zinc and aluminum die-casting methods can help you choose the best alternative for your project. Some of the important differences between zinc and aluminum die-castings are given below.
Overall Weight
The weight of the finished component is a significant design limitation for several people. Both metals are heavier than one may assume in this comparison. However, zinc is slightly heavier than aluminum.
Melting Point
A lower melting point is advantageous for die-casting since it allows you to produce each component with less effort and time. Aluminum cannot be used for hot chamber die-casting, but zinc can since zinc’s melting point is much lower than aluminum’s.
Corrosion Resistance
Another essential need for many designs is corrosion resistance. You’ll need a more corrosion-resistant metal if your component will be used outdoors, in salty environments, or anywhere near acidic processes.
In fact, when comparing the two, zinc offers far more corrosion resistance than aluminum. Many people believe aluminum to be rust-proof, yet this is untrue. Both of these metals would corrode more quickly if they were placed in the same atmosphere as aluminum.
Tooling Life
The fact that aluminum is particularly corrosive in its liquid state is another factor worth mentioning. Your mold will wear out considerably more quickly because molten aluminum constantly fills cavities in a repetitive manner. As a result, tooling life is reduced as compared to zinc, a less abrasive material.
Surface Finishing
What about the finished part’s surface finish? Many people believe that having a shiny bit of metal helps sell the die-cast part. Well, whether a part is composed of aluminum or zinc, you’ll need to go through a finishing stage to polish or smooth it out. The zinc components, however, will become considerably smoother than aluminum ever could.
Costs
Your parts’ total cost will depend on a variety of parameters. You should think about your operating expenses, tooling costs, and the cost of the raw metal you’re using. As we already discussed, zinc tooling is 3–4 times less expensive than aluminum and lasts 10 times longer than aluminum.
Strength
So far, we’ve focused a lot on how superior zinc is to aluminum. It’s quite another situation when it involves strength. Under normal loading factors, aluminum is about four times stronger than zinc.
Is Zinc Die-casting Better Than Aluminum Die-Casting?
The million-dollar question is now: zinc die-casting vs. aluminum die-casting, which is superior?
Aluminum is certainly the better choice because it is much stronger if you require a durable item.
Zinc is a superior material choice if you need parts produced quickly and economically. Additionally, compared to aluminum, it is lighter and more corrosion-resistant.
Conclusion
Both aluminum and zinc alloys have unique features and benefits, but they also have some key differences. Aluminum alloys are softer and more malleable than zinc alloys. Additionally, aluminum alloys are also less resistant to wear and strain. However, zinc alloys are tougher and more durable. Additionally, they have higher corrosion resistance in comparison.
But which is superior? Everything comes down to the needs of your die-casting operation and the intended use. For example, an aluminum alloy could be a preferable option if you require a metal that is both lightweight and corrosion-resistant. However, a zinc alloy would be a superior choice if you require a strong and long-lasting metal.









